Network models
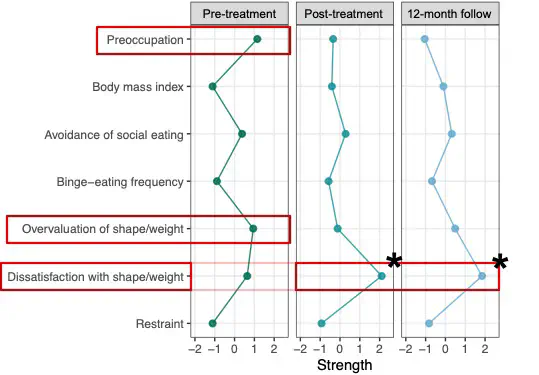 Forrest & Grilo (2022). Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology
Forrest & Grilo (2022). Journal of Consulting and Clinical PsychologySymptoms inter-relate with and (likely) cause one another. Network models statistically model these inter-relations among symptoms. In addition, so many things in life are multiply determined–that is, I can think of very few things where a single X causes a single Y. Thus, another benefit of network models is that they implicitly recognize that outcomes have multiple causes and predictors.
Example questions I tackle within this area include:
- What symptoms of eating disorders seem to “hold up” most other symptoms? What symptoms are most important for eating disorder maintenance?
- Which symptoms might we want to target first and/or hardest to get maximum improvement?
- What symptom relations are true at a group level (i.e., true for most people), true at a subgroup level (i.e., true for only some people), and true only for individuals (i.e., person-specific)?
Example papers within this content area include, but are not limited to:
Forrest, L. N., & Grilo, C. M. (2022). Change in eating-disorder psychopathology network structure in patients with binge-eating disorder: Findings from treatment trial with 12-month follow-up. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 90, 491–502.
Smith, A. R., Forrest, L. N., Duffy, M. E., Jones, P. J., Joiner, T. E., & Pisetsky, E. M. (2020). Identifying bridge pathways between eating disorder symptoms and suicidal ideation across three samples. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 129, 724–736.
Forrest, L. N., Perkins, N., Lavender, J., & Smith, A. R. (2019). Using network analysis to identify men’s central eating disorder symptoms. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 52, 871–884.
Forrest, L. N., Sarfan, L. D., Ortiz, S. N., Brown, T. A., Smith, A. R., & Kaye, W. H. (2019). Bridging eating disorder symptoms and trait anxiety in patients with eating disorders: A network approach. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 52, 701–711.
Forrest, L. N., Jones, P., Ortiz, S. N., & Smith, A. R. (2018). Core psychopathology in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: A network analysis. International Journal of Eating Disorders, 51, 668–679.